What Is Fermentation?
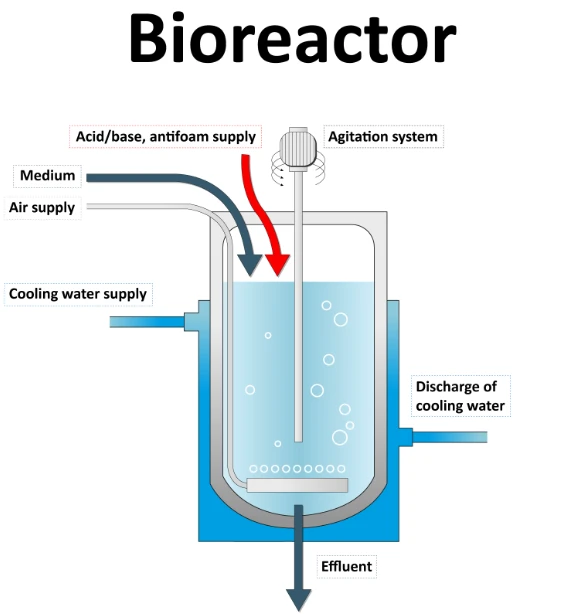
Fermentation is the process of breaking down a substance to its simpler components in order to produce specific chemical and/or physical changes in the media. Fermentation occurs in vessels called bioreactors (or fermenters) that are designed to maintain an optimal environment for the organic material to be cultivated.
Requirements for an optimal fermentation environment
- Very accurate and gentle, controlled flow to maintain cell integrity.
- Precise handling of feed, acid, base and anti-foam fluids.
- Single-use applicability with zero cross-contamination.
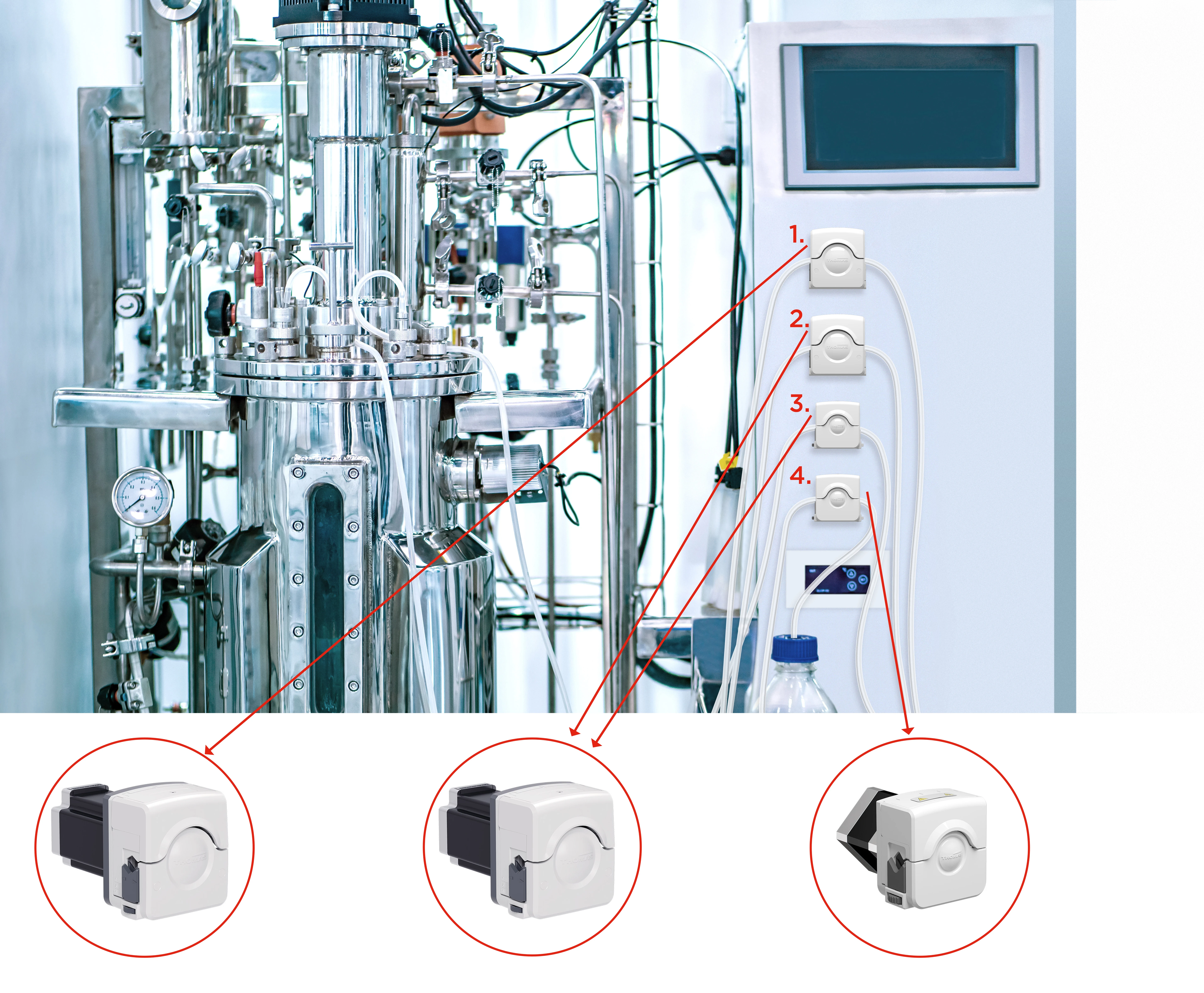
The Role of Bioreactors
As mentioned previously, a bioreactor is the core of biological processes since this is the place where all microbiological and biochemical reactions take place. More specifically, this is a vessel that is designed to provide an effective environment for enzymes or whole cells to transform biochemical matter into products.
What does an effective environment mean exactly?
In terms of bioreactors, this means ensuring a sufficient gas supply, maintaining the right pH-levels and temperature, and providing nutrients, acids, bases, anti-foam or oxygen to successfully maintain growth. To perform all these functions, an appropriate pump technology must be implemented.